927 results found
Featured results



More results
In this Q&A, Philippe explains how PIDG’s 2023-30 Strategy positions action on climate, nature, and sustainability through infrastructure as central to their purpose.
Learn how the transition pathways for sustainable infrastructure link long-term sustainability goals with infrastructure plans.
The GI Hub’s Rory Linehan outlines three critical infrastructure-related areas to watch for at COP28.
Climate change poses a significant threat to infrastructure, with rising sea levels, extreme weather phenomena, and escalating temperatures posing substantial physical risks. These hazards can lead to the degradation of crucial infrastructure assets, undermining social, economic, and environmental stability. Recent analysis by EDHECInfra, as featured in the Global Infrastructure Hub's Infrastructure Monitor report, underscores the scale of the situation. Projections based on current climate and policy scenarios indicate that by 2050, infrastructure assets could see a net value decline of 4.4% on average, and up to 26.7% in the most severe scenarios. This depreciation is a direct consequence of the lack of resilience of global infrastructure to the effects of climate change. The consequences of inaction are far-reaching, affecting not just the financial performance of assets, but also the economic, environmental, and social fabric of communities worldwide. One promising strategy to mitigate these risks involves the adoption of a systemic resilience metrics (SRM) framework tailored specifically to infrastructure.
The development of credit ratings for loans in emerging countries is critical for accessing capital markets
The African Development Bank (AfDB) is mandated to drive social and economic development in Africa through multiple project types including infrastructure
As of April 2019, the IFC successfully raised USD 7.1B from eight global investors through the MCPP, USD 3.6B worth of funds
The International Finance Corporation (IFC) has a mandate to mobilize private financing and is looking to do this through various syndicated products including: B Loans, Parallel Loans and A Loan Participations

Social infrastructure is the best performing segment among all country income groupings, according to new data from Moody’s that provides insights into the debt performance for infrastructure industry sector. Social infrastructure includes healthcare, education and public (community housing, prisons) facilities. The data also reveals transport and energy infrastructure perform differently in relative terms for depending on country income grouping.



The highest recoveries on infrastructure debt default occurs in Africa, the Middle East and Eastern Europe, according to new data from Moody’s shows which regions of the world have the highest and lowest default rates on infrastructure and other project finance debt investments.



Infrastructure equities have an attractive risk-return profile providing a competitive alternative to other investment options.



Merchant infrastructure, larger investors and the transport sector have experienced larger declines in returns due to COVID-19.



Regulatory capital frameworks require banks and insurers to put aside more capital for infrastructure investments than is warranted by their historical credit performance



Public investment in infrastructure is more effective in increasing economic output than other types of public spending



Investment in public transit infrastructure can contribute to creating more inclusive societies. Public transit services are more often used by lower-income households, women and ethnic minorities.





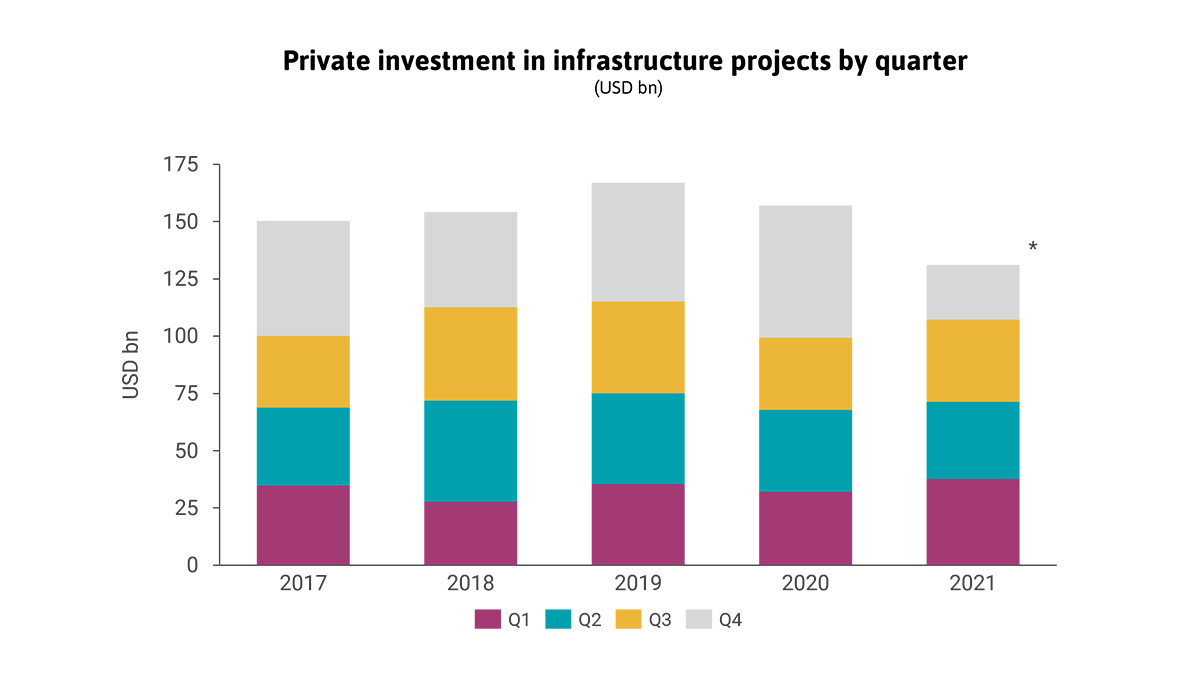
Private investment in infrastructure projects in primary markets was resilient to COVID-19 pandemic shocks



Private investment in infrastructure projects in primary markets has been stagnant for seven years running






 Transformative Outcomes Through Infrastructure
Transformative Outcomes Through Infrastructure







