934 results found
Featured results



More results
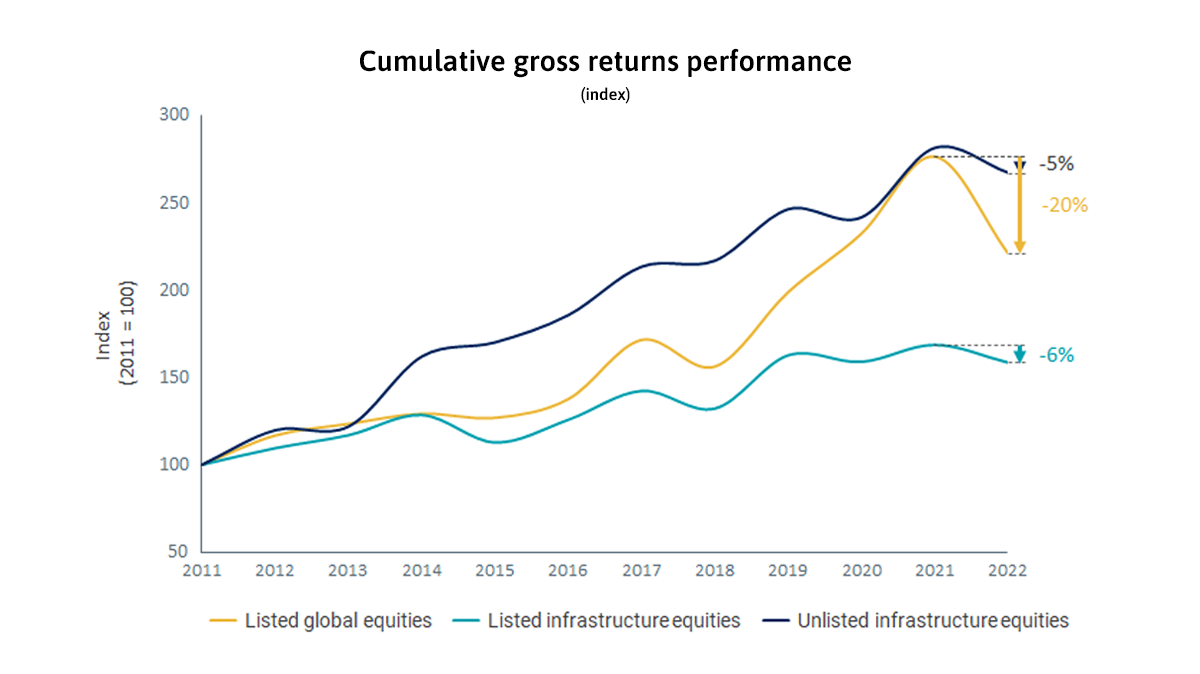
Infrastructure equities provide stronger protection against inflation shocks than the broader equity market. During the rapid inflation shocks in 2022, the return on infrastructure equities was more resilient than that on global equities, which drove private fundraising for infrastructure to record levels.


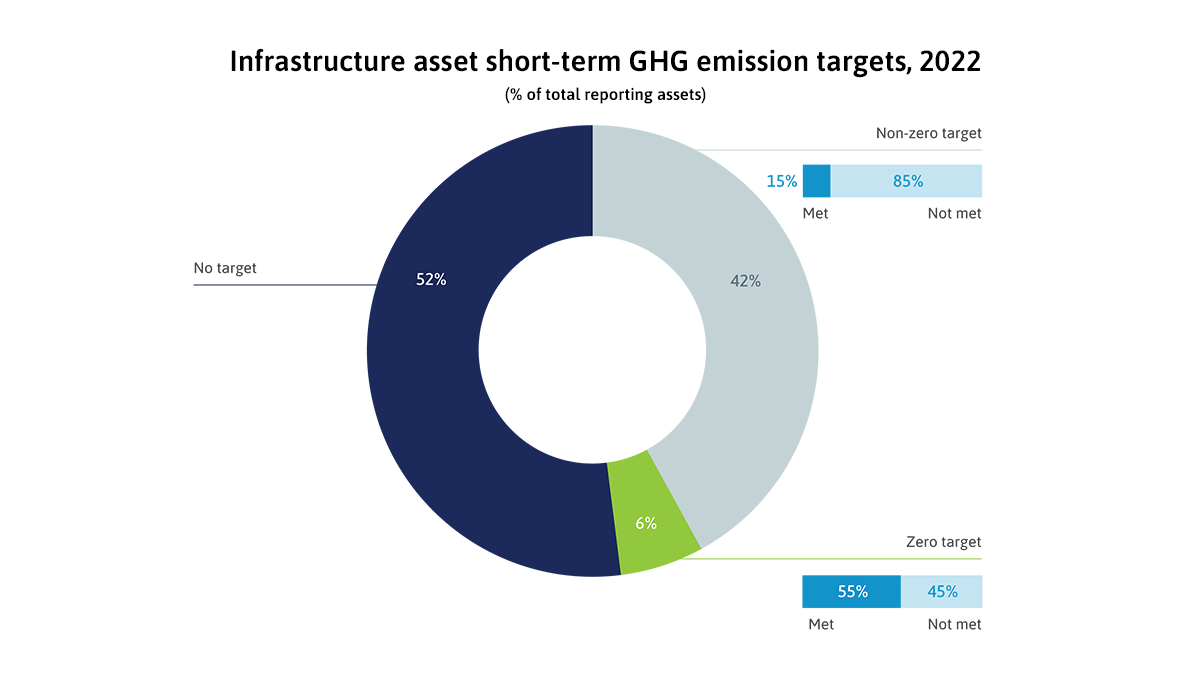
In 2022, infrastructure assets improved their ESG scores in all three pillars of ESG. The scores are encouraging, but they do not mean the assets themselves are more sustainable.



The credit risk metrics for infrastructure debt improved during the COVID-19 pandemic, while those for non-infrastructure debt worsened. The performance of infrastructure loans demonstrates that infrastructure assets are resilient to adverse economic scenarios like pandemics.



The higher risk profile of greenfield infrastructure, and lack of investment-ready project pipelines, make it challenging to deploy private investment to greenfield infrastructure.



The number of primary private infrastructure transactions increased by 18% in 2022, the strongest annual growth since 2017, largely driven by strong investor appetite for projects supporting the clean energy transition. However, growth was mostly being driven by high-income countries in North America and Western Europe, with private investment activity in middle- and low-income countries seeing a lot less momentum with volumes on par with pre-COVID levels.



Regional private investment in infrastructure has seen divergent trends in the post-COVID era, with Western Europe and North America emerging as the two strongest performers, followed by Latin America. Meanwhile Asia, while maintaining relatively stable investment as a share of regional GDP, has experienced the sharpest decline in its share of global private investment in infrastructure, as Western Europe and North America expand their shares. Other regions have seen weaker investment in the post-COVID era (Africa, Oceania, Middle East), or remained stagnant (Eastern Europe).



In low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), around three-quarters of private investment in infrastructure is conducted in foreign currencies, most commonly USD, and only a quarter in local currencies. Brazil dominates local currency transactions in LMICs and has driven a trend increase in the share of local currency transactions in LMIC investment since 2016.


The GI Hub’s InfraTracker aims to help address this data gap by analysing public investment data presented in G20 government budgets


Comparison of InfraTracker data with private investment figures in Infrastructure Monitor also indicate that, in general, governments are the driver of investment in all infrastructure sectors except for energy.


Infrastructure investment undoubtedly has a strong impact on economic growth and development.


This simple and free tool enables project proponents to easily conduct early-stage cost-benefit analyses of bus transport projects.



Infrastructure Monitor identifies and analyses global trends in private investment in infrastructure to inform future investment and policy.



Resources and examples showcase technology’s role in improving infrastructure performance, and solutions to finance technology and manage risk.



This research helps governments and industry ensure that infrastructure investment supports climate mitigation and adaptation, resilience, and inclusive outcomes during challenging economic times.


Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) can be integrated in all stages of infrastructure planning and design to transport users into virtual environments that reveal what designs could look like when constructed and how they would impact upon the existing environment.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) can be used to deploy training programs and assist workers in performing asset inspections and maintenance works.
A water height and flood management system enables local authorities to predict flooding and avoid building infrastructure in high risk areas.
Artificial intelligence (AI) that streamlines processes, documents and data in the flow of goods to reduce duplication, automate handshakes, and improve status accuracy.
V2V technologies are Cooperative Intelligent Transport Systems (C-ITS) that enable communication between vehicles to avoid accidents and and enable the optimisation of traffic flow.
A dynamic tolling algorithm recalibrates toll rates based on traffic congestion and local conditions every few minutes and is a tool to manage traffic demand through pricing.


 Infrastructure Monitor insights
Infrastructure Monitor insights







